목차
- 문제
- 내가 푼 방법
- 자바 코드
- 결과 및 회고
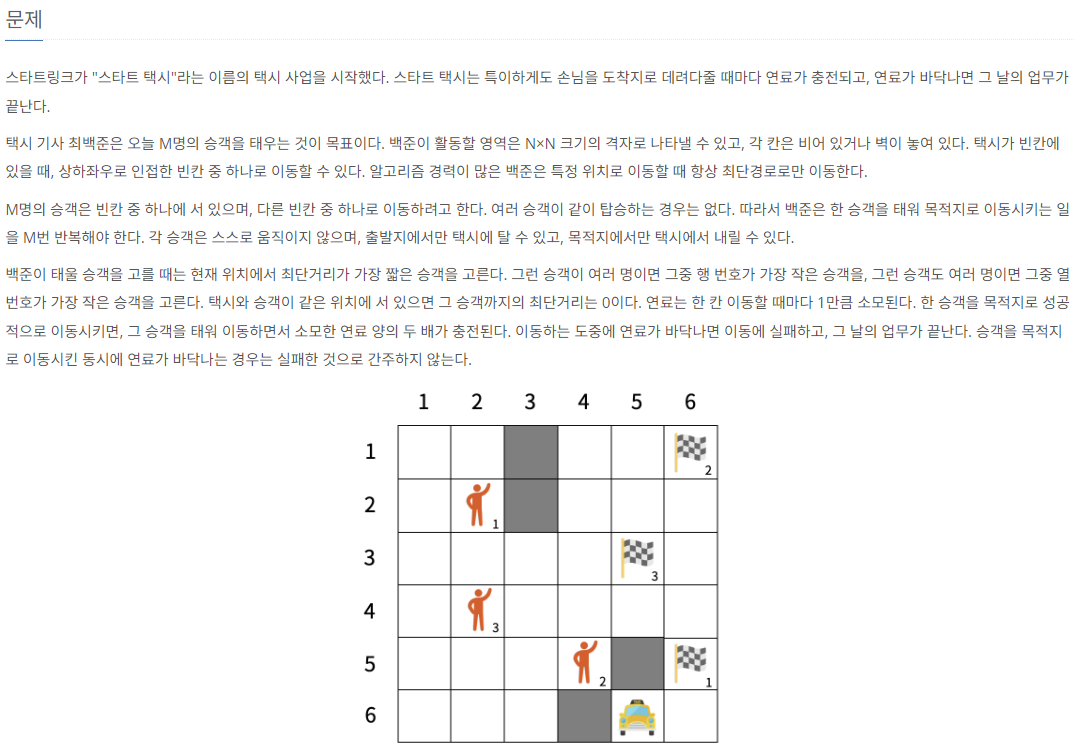
1. 문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/19238
19238번: 스타트 택시
첫 줄에 N, M, 그리고 초기 연료의 양이 주어진다. (2 ≤ N ≤ 20, 1 ≤ M ≤ N2, 1 ≤ 초기 연료 ≤ 500,000) 연료는 무한히 많이 담을 수 있기 때문에, 초기 연료의 양을 넘어서 충전될 수도 있다. 다
www.acmicpc.net
2. 내가 푼 방법
구현이 필요한 BFS 알고리즘 문제이다.
나는 크게 두 개의 함수로 분리했는데, 승객을 태우러 가는 getCustomer 함수와 승객을 도착지에 데려다주는 moveDestion 함수가 여기에 해당한다. 만약 M명의 승객을 모두 이동시키기 전에 연료가 바닥나거나 더 이상 움직일 수 없다면, canArrive 함수에서 S를 -1로 만든 후에 break;문을 통해 빠져나온다.
public static void solution() {
while (M-- > 0) {
Tuple customer = getCustomer();
if (!canArrive(customer)) break;
Tuple dest = moveDestination(map[customer.x][customer.y]);
if (!canArrive(dest)) break;
S += dest.t * 2;
}
}
public static boolean canArrive(Tuple dest) {
S -= dest.t;
if (dest.x == -1 || dest.y == -1 || S < 0) {
S = -1;
return false;
}
return true;
}
이제 각 함수들을 설명할건데, getCustomer 함수에서는 우선순위 큐를 이용해 가장 가까운 승객을 고른다. 이때 중요한 것은 택시 기사 좌표인 driver를 승객 위치로 저장해 두는 것이다.
public static Tuple getCustomer() {
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[N][N];
PriorityQueue<Tuple> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
int[] dx = {0, -1, 0, 1};
int[] dy = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
queue.add(driver);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Tuple t = queue.poll();
int x = t.x;
int y = t.y;
int time = t.t;
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= N || y >= N) continue;
if (map[x][y] == 1 || visit[x][y]) continue;
visit[x][y] = true;
if (map[x][y] > 1) {
driver = new Tuple(x, y);
return t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
queue.add(new Tuple(x + dx[i], y + dy[i], time + 1));
}
}
return new Tuple(-1, -1);
}
moveDestination 함수에서 중요한 것은 map[driver.x][driver.y] = 0; 코드로 승객을 지도에서 지워주는 것이다. 그 후, 도착지까지 거리를 구해 빠져나오면 된다.
public static Tuple moveDestination(int idx) {
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[N][N];
PriorityQueue<Tuple> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
int[] dx = {0, -1, 0, 1};
int[] dy = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int ex = destination.get(idx).x;
int ey = destination.get(idx).y;
queue.add(driver);
map[driver.x][driver.y] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Tuple t = queue.poll();
int x = t.x;
int y = t.y;
int time = t.t;
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= N || y >= N) continue;
if (map[x][y] == 1 || visit[x][y]) continue;
visit[x][y] = true;
if (x == ex && y == ey) {
driver = new Tuple(x, y);
return t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
queue.add(new Tuple(x + dx[i], y + dy[i], time + 1));
}
}
return new Tuple(-1, -1);
}3. 자바 코드
깃허브 풀이 주소 : https://github.com/geujeog/BOJ/blob/main/B19238.java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
static int N, M, S;
static int[][] map;
static Tuple driver;
static Map<Integer, Tuple> destination;
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
solution();
output();
}
public static void solution() {
while (M-- > 0) {
Tuple customer = getCustomer();
if (!canArrive(customer)) break;
Tuple dest = moveDestination(map[customer.x][customer.y]);
if (!canArrive(dest)) break;
S += dest.t * 2;
}
}
public static Tuple moveDestination(int idx) {
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[N][N];
PriorityQueue<Tuple> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
int[] dx = {0, -1, 0, 1};
int[] dy = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int ex = destination.get(idx).x;
int ey = destination.get(idx).y;
queue.add(driver);
map[driver.x][driver.y] = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Tuple t = queue.poll();
int x = t.x;
int y = t.y;
int time = t.t;
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= N || y >= N) continue;
if (map[x][y] == 1 || visit[x][y]) continue;
visit[x][y] = true;
if (x == ex && y == ey) {
driver = new Tuple(x, y);
return t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
queue.add(new Tuple(x + dx[i], y + dy[i], time + 1));
}
}
return new Tuple(-1, -1);
}
public static boolean canArrive(Tuple dest) {
S -= dest.t;
if (dest.x == -1 || dest.y == -1 || S < 0) {
S = -1;
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static Tuple getCustomer() {
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[N][N];
PriorityQueue<Tuple> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
int[] dx = {0, -1, 0, 1};
int[] dy = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
queue.add(driver);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Tuple t = queue.poll();
int x = t.x;
int y = t.y;
int time = t.t;
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= N || y >= N) continue;
if (map[x][y] == 1 || visit[x][y]) continue;
visit[x][y] = true;
if (map[x][y] > 1) {
driver = new Tuple(x, y);
return t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
queue.add(new Tuple(x + dx[i], y + dy[i], time + 1));
}
}
return new Tuple(-1, -1);
}
public static class Tuple implements Comparable<Tuple> {
int x;
int y;
int t;
public Tuple(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Tuple (int x, int y, int t) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.t = t;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Tuple t) {
if (this.t == t.t) {
if (this.x == t.x) {
return this.y - t.y;
}
return this.x - t.x;
}
return this.t - t.t;
}
}
public static void output() throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
bw.write(S+"");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
public static void input() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
S = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N][N];
destination = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
driver = new Tuple(Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1, Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1);
for (int i = 2; i < M+2; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int sx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1;
int sy = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1;
int ex = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1;
int ey = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1;
map[sx][sy] = i;
destination.put(i, new Tuple(ex, ey));
}
br.close();
}
}4. 결과 및 회고
내일부터는 DP 위주로 풀어야겠다.
'문제풀이 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] BOJ 백준 17472번 - 다리 만들기 2 (1) | 2024.01.04 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] BOJ 백준 2638번 - 치즈 (2) | 2024.01.04 |
| [JAVA] BOJ 백준 17143번 - 낚시왕 (2) | 2024.01.03 |
| [JAVA] BOJ 백준 1939번 - 중량제한 (1) | 2024.01.03 |
| [JAVA] BOJ 백준 2146번 - 다리 만들기 (1) | 2024.01.03 |




댓글